| 1.6.2 | |||
| Circle Numbers | |||
| home page | |||
|
Circle numbers represent magnitude using a depth-value notation that supports a maximally factored form, as opposed to conventional Hindu-Arabic numbers that use place-value to represent magnitude in a polynomial form. Both use a uniform base; both support an arbitrary choice of base value. The factored circle form provides distinct computational advantages, at a slight cost to ease of readability. Maximally factored numbers are clumsy when expressed in conventional notation, but quite elegant when expressed in a boundary notation. More fundamentally, boundary notation shows that the foundational properties of group theory are largely syntactic. |
|||
| boundary math | |||
| numerics | |||
|
|
|||
| number systems | |||
| ∆ circle numbers | |||
| graph numbers | |||
|
|
|||
| links | |||
| site structure | |||
|
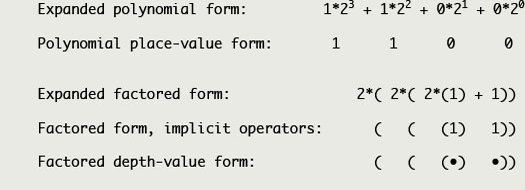
Conventional polynomial and factored boundary forms of binary twelve:
Three animations follow. They each display the same materials, but with varying degrees of condensation. CIRCLE NUMBERS ANIMATION (complete version, 11 minutes) CIRCLE NUMBERS ANIMATION (condensed version, 4 minutes) ADDITION AND MULTIPLICATION OF CIRCLE NUMBERS (short version, 2:20 minutes) |
|||